- Blackjack is played somewhat differently in the land casinos of America and Europe. One of the significant differences lies in how the dealer’s cards are dealt. In American casinos the dealer deals himself two cards, one of which is face up and the other is face down. The face down card is called the hole card.
- Like collusion partnerships in poker, playing the exposed hole-card at blackjack is considered cheating in the majority of land-based gaming areas, but conversely, it is almost impossible to.
In this video, we explain exactly what blackjack dealer tells and hole carding are and how you can and should use them to gain an advantage on the house.
Card counting is one of the most famous advantage-play methods in gambling. In fact, a number of Hollywood movies include card counting scenes or are based entirely on this technique.
Skilled counters can gain anywhere from a 0.5% to 1.5% edge over the house, which leads to good profits over time.
Given card counting’s fame, the mainstream population and even many blackjack players themselves think that this is the only way to gain an edge.
But the truth is that you don’t have to count cards to beat blackjack. Instead, you can use one of several other advantage-play techniques to win.
I’m going to discuss how hole carding, shuffle tracking, ace sequencing, and edge sorting can help you beat the game. I’ll also discuss if any of these advantage-play methods are better than card counting.
Hole Carding
Blackjack dealers at North American casinos deal themselves one face-up and one face-down card. The face-down card is referred to as the hole card because it’s not visible to players.
The dealer is the only person at the table who sees the hole card, because they check for a natural blackjack before players act.
Given that you don’t see the hole card, you’re basing blackjack decisions on incomplete information.
Basic strategy helps you narrow the gap between the house and yourself. But you’re still at a slight disadvantage when using perfect basic strategy.
Enter hole carding: an advantage-play technique that involves spotting the dealer’s hole card. If you see their hole card, you can gain up to a 13% advantage.
Any dealer who consistently offers players a chance to see this is called a “flasher.” These dealers, through one mistake or another, allow players to gain a big advantage by flashing their hole card.
The best way to spot these dealer flaws is by sitting in the right seat and paying close attention to every hand.
Most players don’t pay attention to when the dealer peeks for blackjack or deals themselves the hole card. But by doing so, this gives you a tremendous advantage at a flasher’s table.
Spotting the dealer’s face-down card when they peek for a blackjack is called “first-basing” or “third-basing.” Spotting the hole card when it’s slid under the up-card is called “front loading.”
Many hole-carders sit at first base, which is the first seat to the dealer’s left. This gives you the best chance at seeing a right-handed dealer’s hole card.
The other popular hole-carding seat is third base, which is to the dealer’s immediate right. This is the best spot to see a left-handed dealer’s face-down card.
It also helps if you can gain a vantage point closer to the table felt. The more level your eyes are with the table, the better chance you have of seeing the hole card.
Shorter players have an advantage in this regard because they’re naturally closer to the table felt. Taller players often lean back to improve their vantage point.
Of course, the key is to do so in a subtle manner. Being obvious about leaning back or slouching draws attention to your hole-carding efforts.
Another thing that you need to be careful of is over-using your advantage. Sometimes you should ignore the info you gain when using basic strategy because some plays look too suspicious.
Here’s an example.
- Your first two cards total a hard 8
- The dealer’s up-card is a 10
- You see that the dealer’s hole card is 2
- The optimal play is to double down against the dealer’s 12
- But no regular player is going to make this decision because they’re not supposed to have this info
The last thing that you want to do is continue taking advantage of plays like this, especially when your dealer is a consistent flasher.
If the casino finds out that a dealer is consistently flashing cards and helping a player(s) win, one of two things will happen.
- 1. The dealer will receive better training
- 2. The dealer will be fired if flashing becomes a consistent problem
In either case, the work you put into finding a flasher goes out the window. And this is hardly worth taking advantage of a few suspicious plays that you should let go.
Players need to think long term and realize what kind of profits they can make by continuing to play at the dealer’s table. Avoid decisions that are too far outside the bounds of regular strategy.
It’s hard to find a consistent flasher. Casinos train dealers on how to deal without giving players a chance to see their hole card.
Nevertheless, some dealers either don’t pick up enough skills in training or become lackadaisical over time.
The best place to start when looking for flashers is casino-heavy cities like Las Vegas, Atlantic City, and Reno. This enables you to bounce from casino to casino within a single shift.
Odds are that you’re not going to find a flasher within your first few hunts. But once you do find one, note what shift they work and make it a priority to play at their table.
Shuffle Tracking
In the 1960s and ‘70s, Las Vegas casinos began implementing shoe games. The idea was to hinder card counters by forcing them to count through multiple decks in each shoe.
Casinos thought that they solved their card counting problem with shoe blackjack tables. But card counters merely adjusted their strategy, and other techniques such as shuffle tracking were born as well.
Shuffle tracking refers to tracking specific cards, or a sequence of cards, through multiple shuffles. Shuffle trackers monitor where 10s and face cards (a.k.a. high cards) are throughout the coming rounds.
Much like card counting, the goal is to bet more when the shoe is abundant in high cards. When used properly, shuffle tracking is much more effective than counting.
But this technique is also very difficult to use, because you must know an advanced strategy on top of card counting.
The basic idea behind shuffle tracking is that shuffles aren’t random, and you can track certain cards after a shuffle.
You might think, “Can’t dealers just shuffle more to make decks more random and stop shuffle trackers?” But many casinos don’t like their dealers wasting too much time with shuffles, because this slows the game and lowers profits.
Blackjack dealers commonly use a “zero shuffle,” where cards are separated into piles, with the shuffling only being done between the piles (i.e., the dealer grabs two piles and riffles them). This means that the ace of hearts, for example, would have a high chance of only being in one or two sections of the shuffled shoe.
Card counting comes in because you want keep track of the count in different discard sections. I’ll start this explanation by looking at the point values assigned in the Hi-Lo counting method.
- 2 through 6 = +1
- 7 through 9 = 0
- 10 through ace = -1
You can use other card counting systems with shuffle tracking. But the Hi-Lo is a popular counting strategy that’s easy to use.
As you may know, high cards favor the player by improving their chances of getting a natural blackjack payout. This advantage comes from the fact that players get either a 3:2 or 6:5 bonus with a natural.
Meanwhile, low cards reduce the dealer’s chance of busting out while they try to reach a hard 17. Anything that increases the dealer’s odds of winning is bad for players.
The premise is to make higher bets when the shoe is rich in aces and 10-value cards (i.e., positive count) and bet the table minimum when the shoe contains more low cards (i.e., negative count).
The overall positive or negative count is referred to as a “running count.” But Hi-Lo system users convert this into a “true count,” which accounts for the number of unplayed decks in the shoe.
Here’s an example:
- Your running count is +8
- There are 4 decks remaining
- 8/4 = +2 true count
Card counting and shuffle tracking come together when players have a good idea of what card values are left in the shoe based on their count. If they can take this a step further by visually tracking high cards and finding them bunched together, they gain an even greater advantage.
One big benefit of shuffle tracking is that it’s harder to spot than card counting.
Sure, you’re still increasing bets during favorable situations. But your increased bets come in a shorter span once 10-value cards and aces emerge in clumps.
Another advantage is that you can gain up to a 50% advantage with perfect shuffle tracking.
No player will have this edge all of the time. But an expert shuffle tracker may gain between a 10% and 30% long-term edge, depending upon the dealer and shuffling style they’re using.
The downside is that shuffle tracking is extremely difficult to pull off. You not only need to keep a good count, but also follow the deck with your eyes and understand how high cards will disperse after shuffles.
Be prepared to practice for quite some time in order to become an expert shuffle tracker. Even then, you need to be good enough to pull this off with a high degree of certainty.
In other words, some players fool themselves into thinking that they’re gaining an edge, when they’re really not doing anything special.
Another drawback is that not every casino trains their blackjack dealers in a shuffle that can be exploited. Some casinos use a 2-pass shuffle, where they go through two rounds of riffling and restacking.
2-pass shuffles make it harder to track cards during a shuffle. Ideally, you want a one-pass shuffle to cut down on the randomness of the shoe.
One more point worth making is that you can’t shuffle track with a continuous shuffling machine (CSM). That said, look for hand-shuffled shoes with one-pass shuffles.
Ace Sequencing
Ace sequencing is a different type of card tracking, where you try to remember what cards are on top of the ace in the discard pile. You then make larger bets when you see these cards come out in hopes of being dealt an ace.
Like shuffle tracking, ace sequencing is a difficult pursuit. The best ace trackers can remember up to a dozen card sequences in each shoe, thus greatly improving their chances of catching aces.
If you know that you’re likely to be dealt an ace, you can gain up to a 50% advantage on the house. When you’re dealt an ace, you have a 31% chance of getting a 10-value card and completing a natural blackjack.
But becoming a great ace tracker is hard because there’s not many materials on the matter – unlike with card counting. Additionally, it takes a while to learn how to properly execute this concept.
Ace sequencing begins with watching discard segments so that you can guess what clumps might appear intact after a shuffle. You also want to watch where aces go into the discard tray, so that you have a good idea on when an ace will be dealt in a segment.
Finally, you want to remember 2-3 cards that are placed on top of the ace in the discard try. Dubbed “key cards,” these are what you watch for after the deck is shuffled.
You then increase your bet when you see the key cards and can anticipate an ace being dealt.
But keep in mind that ace sequencing is just like shuffle-tracking in that it doesn’t work when your table has a CSM.
Edge Sorting
Edge sorting is an advantage-play technique that was popularized by poker pro Phil Ivey. Along with his partner Cheung Yin Sun, Ivey won over $20 million collectively from Crockfords and the Borgata.
Lawsuits ensued, and the court sided with both casinos on the matter. But this was only after Ivey’s case was heavily scrutinized by casino security.
That said, it’s theoretically possible for blackjack and other card players to win money with edge sorting.
This technique involves spotting flaws on card backs and using this information to predict card values before they’re revealed.
But you can’t just walk into the casino and expect to find a flawed deck to take advantage of. Instead, you need to know about design flaws in specific manufactured decks and determine where these decks are used.
This is how Cheung was able to help Ivey win millions of dollars. She analyzed a purple Gemaco deck for hours and became good at spotting the design flaws.
These flaws often come in the following form.
- One side of certain card backs will feature half-diamonds on the edge
- Other cards may have full diamonds on the edges
- These flaws are easiest to spot when the flawed side is rotated towards you
- The goal is to figure out which values have an irregular diamond pattern on the back
Edge sorting works best when cards are rotated 180 degrees because this makes it easier to see the diamond patterns. This is why Ivey specifically requested that cards be rotated 180 degrees under the guise of superstition.
But Ivey is a high-stakes gambler who can make these kinds of requests. The average player doesn’t have this sway and won’t have a chance with edge sorting.
Unless you’re a high-stakes blackjack player, then you can’t gain an advantage through this technique through special requests. Even when you can make these requests, casinos will be on guard due to the fame associated with Ivey’s case.
Do Any of These Advantage-Play Methods Beat Blackjack?
All of the blackjack advantage-play techniques covered above can give you a greater edge than card counting.
You can gain up to a 50% advantage in the case of both shuffle tracking and ace sequencing. Hole carding can also give you a nice edge worth up to 13%.
I can’t find exact figures on what advantage a player can gain with edge sorting. But based on how well Ivey did, I’m assuming that you can earn over a 20% advantage with it.
Compared to all of these techniques, card counting is a much tougher grind. The average skilled card counter only gains a 1% advantage.
This means that you’ll experience almost as many losing sessions as you do winning ones. Because of this, card counters need large bankrolls worth $30,000 or more to survive variance with any degree of certainty.
But the good thing about counting is that it’s easier to pull off than any of the methods I covered above. Furthermore, you can find more blackjack games that are susceptible to card counting.
Contrast this to hole carding, shuffle tracking, ace sequencing, and edge sorting, where you need much more specific conditions to win.
I’m not saying that you shouldn’t try these advanced strategies. This is especially the case with hole carding, shuffle tracking, and ace sequencing, which work with great success in the right games.
But be aware that you’ll need to put in more work with these techniques to properly use them.
Conclusion
You’ve likely heard stories of card counters getting kicked out of casinos. In fact, the movie 21 dedicates multiple scenes to the casinos’ pursuit of the MIT Blackjack Team.
The same holds true of any other blackjack advantage-play method you use, whether it be hole carding, shuffle tracking, or edge sorting.
Casinos are private establishments that can refuse service to blackjack players. And if they determine that you’ve gained an advantage in any form, they’ll ask you to leave.
This makes it important to blend in and act like a normal player if you do gain an advantage. If your edge is large enough, you might even consider messing up a few plays just to look like an average recreational player.
Above all, make sure that you have an advantage first. Then you can concentrate on a persona to use to avoid casino detection.
But before you embark on a quest to become a pro, I recommend playing some low-stakes blackjack while you figure the game out.
You can use basic strategy while keeping an eye on the dealer’s hole card, flawed decks, or shuffle-tracking opportunities. This is a nice way to transition from being a regular player to getting an edge on casinos.
Please enable JavaScript to view the comments powered by Disqus.In card games, hole carding is the obtaining of knowledge of cards that are supposed to be hidden from view. The term is usually applied to blackjack but can apply to other games with hidden hole cards, like three card poker and Caribbean stud poker. So long as it does not involve the use of a device like a mirror or actions like touching the dealer's cards, in most jurisdictions hole carding is a legal form of advantage gambling in casino table games. In other games, like stud poker, casinos normally have rules against rubbernecking or having a confederate stand behind an opponent to signal hole cards.
Blackjack players must usually make playing decisions based on only seeing one of the dealer's cards (the upcard). But if the dealer's hole card is spotted, a player who plays correctly has a theoretical advantage of up to 13% instead of the normal player disadvantage of around 0.5%. A hole-card player will often choose not to make certain plays, such as hitting a hard 19 against a dealer 20, so as not to reveal that he can see the dealer's hole card.
This technique is not applicable in most games outside of the United States where the second dealer card is normally not dealt until all players have played.
Strategies[edit]
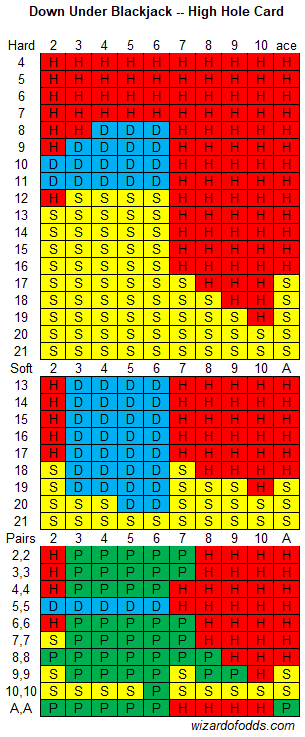
A normal blackjack strategy has ten columns, for an ace through dealer ten value card. Strategy tables for hole carding differ from normal blackjack tables as they include a column for each possible total dealer hand instead of simply the visible card. Below is a sample hole card hit/stand table for six decks, stand on soft-17. The columns are based on the dealer hand and the rows based on the player hand. Green denotes a hit.
First-basing and spooking[edit]
Hole Card Play Blackjack
One method of hole carding is to peek at the card when the dealer checks the hole card for blackjack. This is called 'first-basing'.[1] A modification called 'spooking' refers to a partner with a better view peeking at the hole card in the same circumstance and communicating the information to the player. Peeking devices have made these methods largely obsolete.[2]
Front-loading[edit]
Front-loading refers to observing the hole card as it is slid under the upcard.[3] Newer methods of hole-carding concentrate on observation before the down card is placed under the upcard. This provides information about the card even if the dealer upcard is not a ten or an ace. The advantage varies depending on the rules, the percentage of cards seen, and the strategies used.
Partial information[edit]
At times the player will see a corner of the hole card, but not enough to determine the exact card. For example, if there is no pip in the corner, the card may be an ace, 2 or 3. Or, if there is a pip in the corner, it is a 4-10, but not a face card. To make use of this additional information, a different set of strategy tables must be used depending on the set of possible cards in the hole.[4]
Blackjack Hole Card Strategy
Below is a sample blackjack, partial hole card hit/stand table for two decks. The columns are based on the dealer upcard and the rows based on the player hand. Partial hole card tables contain ten columns as the dealer's total hand is not known with complete certainty. A different set of tables must be used depending on the information acquired from the hole card. In this table, the hole card is a six or seven. Green denotes a hit. One might note that this table bears little resemblance to standard blackjack strategy.
Next card play[edit]
Hole carding generally refers to knowing the dealer’s hole card. Next card play refers to knowing the next card to be dealt. If a round has not started, and a player knows what his or her first card will be, one can simply alter one's bet depending on the value of that card. In a game like blackjack, if the dealer has already dealt a player's first two cards, and the player knows the next card to be dealt, it becomes possible for playing decisions to be altered to include this additional information.[4]:255 Strategies are significantly more complex as there exists a different strategy table for each possible next card. Strategies may also differ depending on a player's position in the dealing rotation:
- First Seat – If the player does not take the known card, another player gets it.
- Last Seat – If the player does not take the card, the dealer may draw it. This also applies in a situation where no player to one's left is likely to draw a card.
- No hole card – In a no-hole-card game, if the player does not take the card, it may become the dealer’s second card.
Hole Card In Blackjack
Other methods[edit]
- Warped cards – In a casino where a blackjack dealer bends the hole card to check for a blackjack, the cards can become warped. The warps can be later used to determine the value of a face down card. This method is largely obsolete as most casinos use devices instead of bending cards to determine dealer blackjacks, and cards are regularly replaced with new decks.[5]
- Dealer tells – When a blackjack dealer checks for a blackjack, some dealers may give clues as to the value of the down card, akin to Poker tells. Again, most casinos now use devices to check the down card, rendering this obsolete in most casinos.[6]
- Peeking at other players' cards – Depending on the game and casino, this may or may not be acceptable and may aid player decisions.
- Counting by inference – In blackjack where player cards are dealt face down, the actions of other players can provide clues as to their hidden cards. This is less valuable in modern casinos due to the fewer number of single-deck games and reduction in penetration (how deeply the dealer deals before shuffling.)
Notes[edit]
- ^Blaine, Rick. Blackjack blueprint : how to play like a pro-- part-time. Huntington Press. p. 154. ISBN0-929712-16-1.
- ^Snyder, Arnold. The big book of blackjack (1st ed.). Cardoza Pub. p. 311. ISBN1-58042-155-5.
- ^Uston, Ken. Million dollar blackjack (6th rev. print ed.). Gambling Times. p. 197. ISBN0-89746-068-5.
- ^ abGrosjean, James. Exhibit CAA : beyond counting (1st ed.). South Side Advantage Press, LLC. p. 279. ISBN0-9790061-4-7.
- ^Humble, Lance; Cooper, Carl. The world's greatest blackjack book (Rev. ed.). Doubleday. p. 141. ISBN0-385-15382-1.
- ^Snyder, Arnold (2005). Blackbelt in blackjack : playing 21 as a martial art (3rd ed.). New York: Cardoza Pub. ISBN978-1580421430.